AAVE, Curve and Sushiswap: Why are the hosts of Defi projects integrated with Polygon

The increase in gas value in the Ethereum network has spurred competition between projects developing scaling solutions.
At the beginning of the year, Binance Smart Chain showed more than confident growth. This EVM -compatible platform provides quick and inexpensive transactions, but its great drawback is high centralization.
Soon, the Polygon ecosystem (previously Matic Network), committed by advanced innovations and positioning itself as “Internet blockchains” gained popularity. Thanks to almost instant transactions and extremely low commissions, the project in a matter of months entered the first three leading protocols at the cost of blocked funds (TVL).
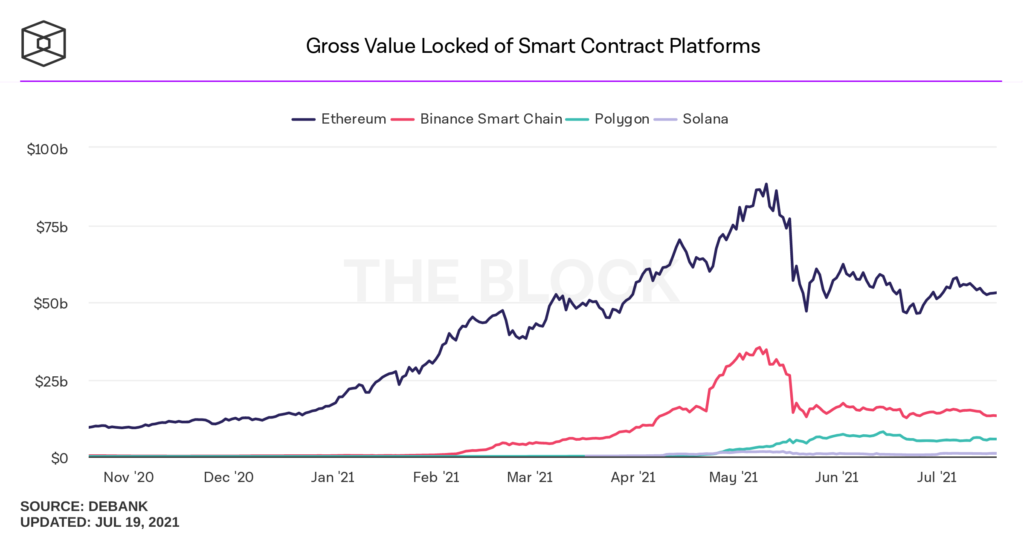
FORKLOG figured out the reasons for the growth of the ecosystem and the features of Polygon architecture.
- In recent months, the Polygon ecosystem has demonstrated an impressive growth, expressed in increased onchain activity, growth in the price of native token, the emergence of many Defi projects and integrations.
- The Polygon Pos Chain system has specific features that put it far beyond the framework of simple Sidchan.
- The developers have to add support for Optimistic Rollups, ZK-Rollups and Validum, ultimately becoming an aggregator of scaling solutions.
Polygon explosive growth
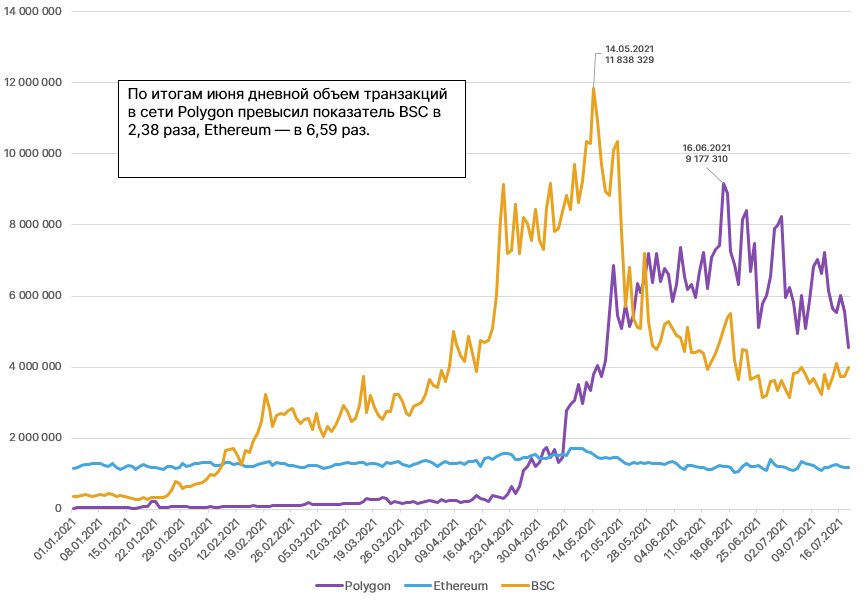
Despite the very young age of the ecosystem, the daily volume of Polygon transaction significantly exceeded the indicators of Binance Smart Chain and Ethereum.
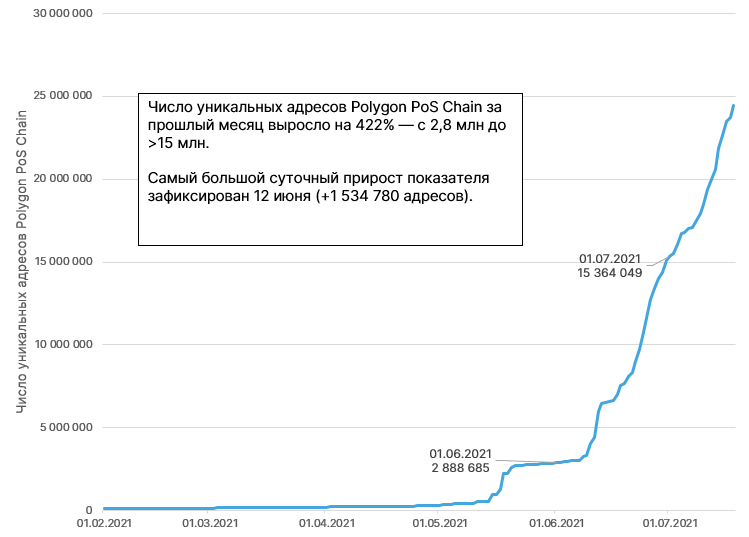
During June, the number of unique addresses Polygon quadrupled. This is a sign of an increase in the user base and general activity in the ecosystem.
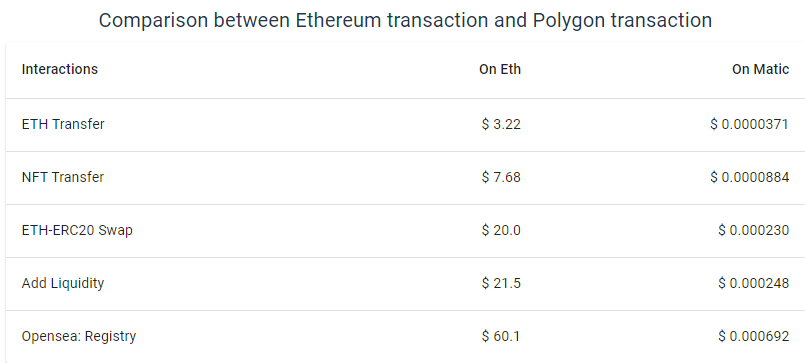
High onchain-activity is due to quick and cheap transactions. The average cost of the operation on the Polygon network is hundreds of times lower than Ethereum is an undeniable competitive advantage. The comparison is given in the table below.
The success of Polygon also contributes to the network effect due to integration with Sushiswap, Aave, Curve, 1inch and many other Defi platforms. The total TVL ecosystem based on Polygon, numbering more than 350 projects, exceeds $ 5 billion.
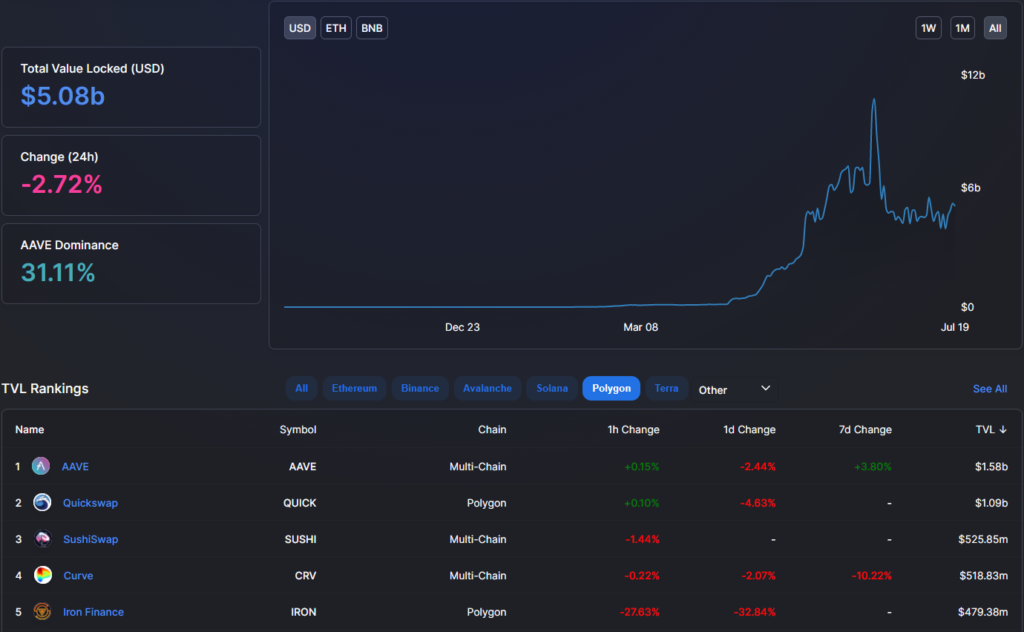
AAVE is a landing protocol that also leads in the Ethereum emission, according to Defi Pulse.
Quickswap – an analogue of Uniswap and the host of DEX based on Polygon.
Iron Finance is a protocol that also works on Binance Smart Chain, which has a partially secured Iron stablecoin, gently tied to the US dollar. In June, a project, among the participants of which billionaire Mark Kyuban, was subjected to “banking panic”.
Curve – a platform focused on stabiblcoins based on an automatic market maker (AMM) mechanism.
Dfyn is a platform that positions itself as a network of decentralized exchanges, including on the basis of second -level solutions.
Beefy Finance – Binance Smart Chain Farm Optimizer.
Balancer-non-castodial portfolio manager and AMM platform.
Kyber – "Hab of target liquidity protocols for various options for using Defi".
Autofarm – DEX aggregator and income optimizer that also supports BSC, Huobi Eco Chain.

Many of the above projects originally worked on the basis of Ethereum (for example, Sushiswap, Kyber and Balancer), or Binance Smart Chain (Autofarm). Polygon’s integration helped them strengthen the position in the Defi segment. A striking example of this is AAVE, which in recent months has been holding leadership on TVL.
The diagram below is visible the growth of the share of Polygon in the total TVL of various protocols. The June decrease in the BSC share with the growth of the Ethereum segment is also noteworthy.
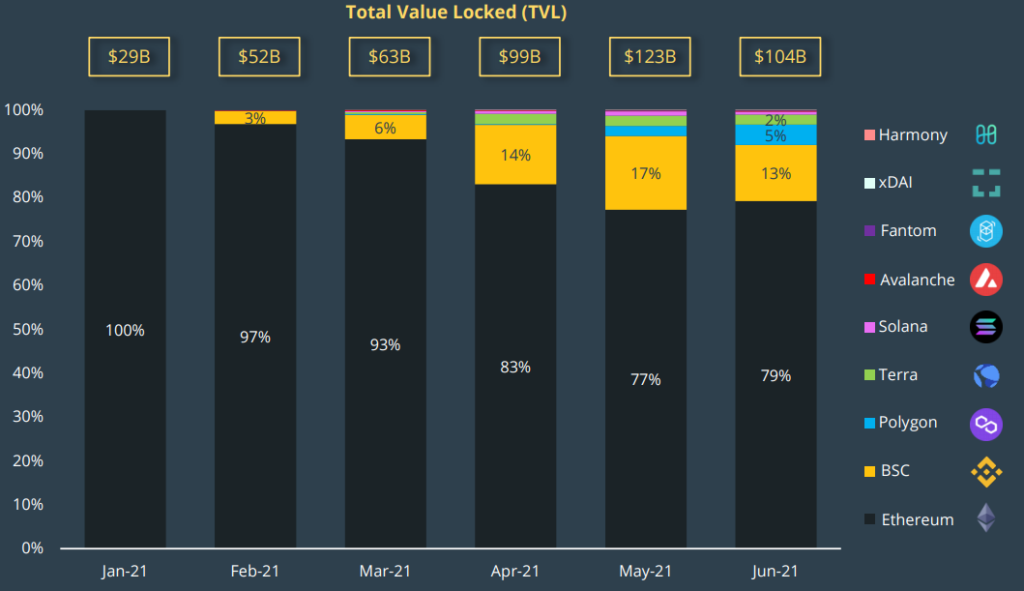
“Polygon has succeeded recently – it is available while most second -level solutions remain in development. AAVE was deployed on Polygon in April, the Curve and Sushiswap platform and Sushiswap platforms soon followed this example, ”said Messari analyst Rashid Saleuddin.
The developers of the "Internet blockchains" comprehensively develop the ecosystem, not limited to various solutions of the second level (Layer-2, L2). In July, the project presented the Polygon Studios unit focused on blockchain games and the NFT Ecosystem. The new structure plans to attract large brands, popular content creators and investors who want to work in the corresponding direction.
The Opensea NFT market, which has recently attracted $ 100 million when estimated at $ 1.5 billion, added the possibility of buying a Polygon assets using a debit or credit card. Integration with the protocol allowed the company to reduce potential transactional costs of users related to gas payment on the Ethereum network.
In April, the Polygon team launched a $ 100 million fund, designed to make decentralized finances more popular, affordable and scalable. According to Sandipa Nailval, in #defiForall Fund will be concentrated to 2% of the total supply of Native tokens (200 million Matic).
What is Polygon under the hood?
The project started in October 2017. Polygon was called Matic Network to rebranding. His co -founders Jainty Ganves, Sandip Nailval, Anurag Arjun and Mikhailo Beli set a goal: to solve the problem of scaling Ethereum.
Initially, the team began work on Plasma Chains – a second -level solution based on their own implementation Plasma. Faced with some difficulties, including the problem of data availability and a long period of withdrawal of funds, the project has moved to the development of POS Chain-Ethereum Sadchain, using the Proof-OF-Stake consensus mechanism.
The result of more than two years of work was the launch of the main network of Matic Network. The project began to attract more and more attention against the background of the growth of commissions on the Ethereum network, which emphasized the acute need to search for reliable and effective scaling solutions.
In February 2021, Matic Network changed the name of the project for Polygon. Rebranding was dedicated to the transition to the concept of an ecosystem that allows you to integrate various scaling solutions-from sideshins with various consensus mechanisms to L2-optovia like Plasma, Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups.
Polygon supports two main types of Ethereum-compatible networks:
- Standalone (autonomous) networks;
- secure (secured) networks using the "Safety as a Service" model.
Autonomous networks They rely on their own protection, they may have their own consensus model like Proof-Of-Stake (POS) or Delegated-Proof-Of-Stake. Such networks are independent and have flexibility, but it is these qualities that become an obstacle to the achievement of a high level of security. For example, POS requires a large number of reliable validators. This type of model is usually suitable for corporate networks and already held projects with strong communities.
Protected networks use the "Safety as a Service" model. Its work provides either Ethereum directly, for example, through the “evidence of fraud (Fraud Proofs) involved in Plasma, or through the bullet of the validators. Protected networks provide the highest level of security, sacrificing some degree of independence and flexibility.
From L2, Polygon is used only by Plasma, however, work is also underway on other second-level scaling technologies. It is quite difficult to integrate them with existing infrastructure, since Plasma and POS frames are not compatible directly with Rollups or Validium.
The changes presented in Lite Paper are aimed at making Polygon a popular scaling tool for EVM-compatible applications that provide a high degree of flexibility for developers and wide possibilities for setting up infrastructure for various types of services.
100 validators work in the Polygon ecosystem, various projects may contact their services. This concept is similar to the Polkadot collective security mechanism.
Polygon architecture is four abstract and component levels or layer.
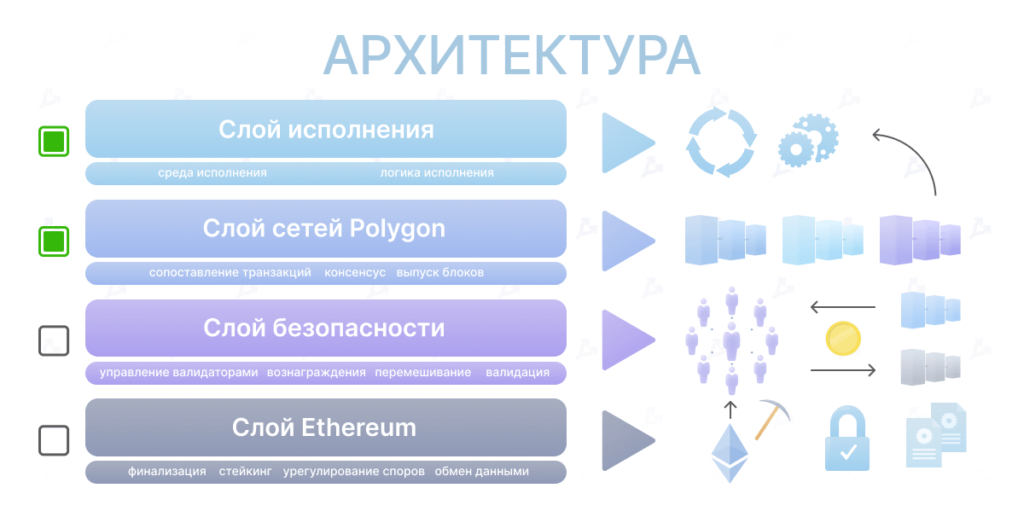
Ethereum layer. Polygon networks can use Ethereum as a basic level, which is characterized by a high degree of security. This level is implemented as a set of smart contracts and is involved for operations such as Finalization, Checkpoint, Stayking, Settlement of disputes and data exchange. It is optional – Polygon networks are not required to use it.
Safety layer – Another optional level that provides the work of the “Validators as a Service” model. It allows Polygon networks to use a set of validators who periodically check the state of systems in exchange for commission reward.
This layer is usually implemented as a metablockchain working in parallel with Ethereum and responsible for registration, distribution of remuneration, shuffling and validation of Polygon networks. It is abstract in nature and can have many implementation options with different properties. The layer can be implemented directly on Ethereum using miners as validators.
Layer of networks. This is the first mandatory level in the architecture of Polygon. It consists of sovereign blockchains, each of which can ensure a comparison of transactions, local consensus and the creation of blocks.
This level ensures the intensity of systems. Developers can create their own layer of networks, or use the level of POS-headlide by Heimdall to launch their applications.
A layer of execution. He is responsible for the interpretation and implementation of transactions in Polygon networks. The layer consists of a subsurface of the environment and the logic of execution. This is an EVM-compatible level, which involves the convenience of integration of applications.
Thus, Polygon can provide various options for systems – with an emphasis on safety, transaction speed, minimization of costs and sovereignty. Given the eternal scalability trille, projects can choose the option that is most suitable for their uses and switch from one solution to another.
This architecture also allows various solutions to Polygon to interact with each other, preventing the creation of disparate, isolated systems.
At the time of writing, Polygon is available only by POS and Plasma networks. The project also provides a set of development tools (SDK), which helps new projects to create flexible and customized scaling solutions.

Matic Plasma Chains It is a solution of the second level based on the framework of scalable decentralized applications Plasma, proposed at one time by Joseph Pun and Vitalik Butaterin.
Plasma uses smart contracts and trees of Merchans to create an unlimited number of daughter chains-copies of the parent network Ethereum. The main blockchain is unloaded by subsidiaries, opening the possibility of implementing fast and inexpensive transactions.
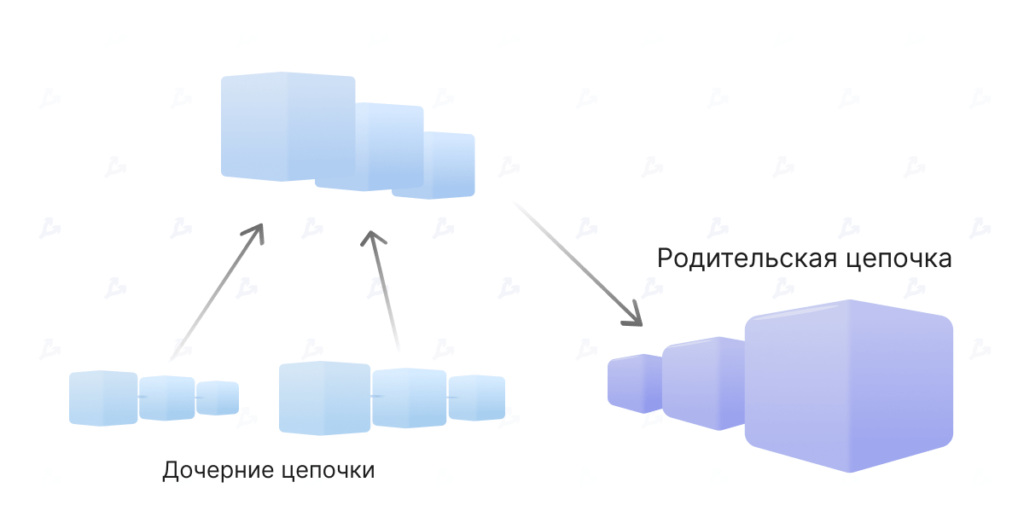
One of the shortcomings of the decision lies in the long period of the withdrawal of funds from L2 – about a week. Plasma cannot be used to scale applications based on complex smart contracts. The solution supports only simple functions like transferring funds and exchange operations.
Matic Pos Chain It is a public (permissionless) sidecchain, working in parallel with Ethereum. Its safety is ensured by the Proof-OF-Stake consensus mechanism with its own set of validators.
Matic Pos Chain also relies on the safety of the ether network when it comes to checkpoints and stakeing. This Sidchan EVM-compatible, which makes it possible to simply and freely integrate with it with Ethereum projects.
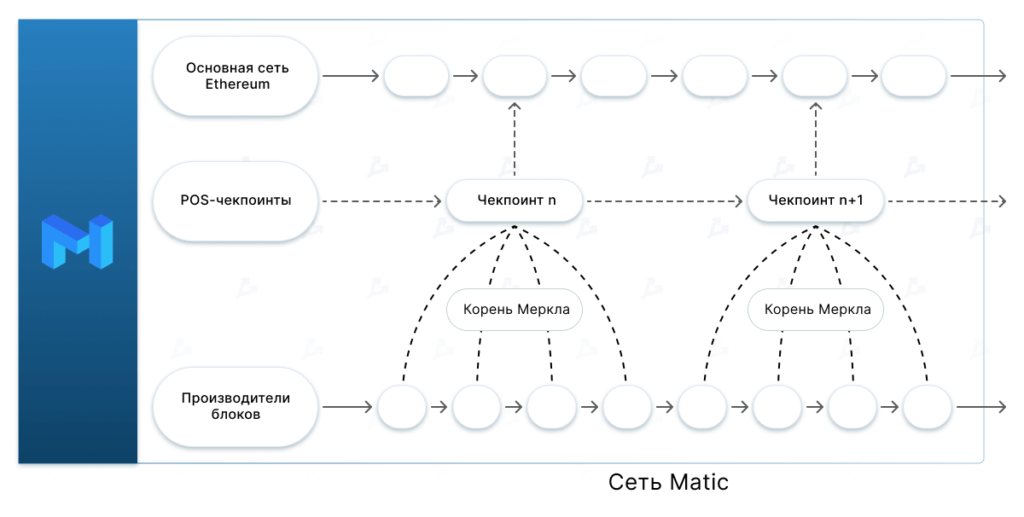
In the process of achieving consensus in Polygon, users-vicacular users are stacked by Matic tokens. Polygon chains provide a mechanism for removing the stained tools (sling). It does not allow stakeholders to offer invalid blocks, verify blocks and carry out transactions in violation of the network rules.
Matic Pos Chain includes two levels:
- Bor – is responsible for aggregation of transactions to blocks;
- Heimdall POS-pos -Supports all validant nodes (stakers), which work parallel to the Matic Network steaking contractions and control validators accounts, produce sling and release awards.
BOR manufacturers of BOR blocks are a subset of network participants who are periodically shuffled by Heimdall validators. These groups are selected from a pool for validation of only a certain set of blocks called Span (site).
Heimdall works on the Tendermint engine, in which data structures and signature scheme are changed. He is responsible for the validation of blocks, the work of the Creators of the Creators of the Blocks and the control of the process of introducing sides-blocks in Ethereum (checkpointing).
This level aggregates the BOR blocks in the tree measure. The summarized data is sent to the main network Ethereum as Committed, fixing the latest state of the Polygon system.
The above mechanism is similar to Optimistic Rollups, where users trust the last state in the Ethereum network, where there are no signs of fraud. However, Polygon uses Sidchan’s architecture, which is associated with some risks. For example, there may be attackers among validators, and bugs in the consensus algorithm are not excluded.
Heimdall validators need to steak Matic tokens in Ethereum before they can engage in checking and ensuring the safety of their network. Checkpoint is carried out for about every 34 minutes. The result of this process should be confirmed by at least two -thirds of the validators. Only after that the data is sent to Ethereum.
Remunerations are distributed between validators in the form of Matic tokens. They include the award for staying and commission for user transactions.
Everyone can participate in validation – for this you need to have at least one Polygon network token. At the time of writing, more than 28% of the project coins are involved in stakeing. It is worth noting that Matic is not a control token – voting is limited by changes in parameters associated with validators.
The important function of the heimdall validators is to synchronize data between the networks.
“State Sync is a native mechanism for reading Ethereum-data from Matic EVM chain. Heimdall level validators receive Statesynced events and transmit them to Bor, ”the documentation on the Matic Network website is indicated.
This event means that there is an update of the state of the main network Ethereum, the information about which must be transmitted to Polygon. The backdressed process is carried out through check -intition.
Thanks to the features of the architecture, Polygon has a very short interval between blocks-2-4 seconds. This provides high throughput.
Not quite Sidchan
The developer and founder of the Finematics portal under the nickname Jakub believes that POS Chain from Polygon is more than just Sidchan. He calls this Commit Chain system.
“When we are talking about Polygon Commit Chain, it should be distinguished with the sidechard, since it has many additional functions that rely on the safety of the main network Ethereum,” the article says on Finematics.
Jakub emphasizes that it was used to be classified as a second level of not only Plasma and Rollups, but also sidechens, since they are all built on top of the main network.
“After some time, the Ethereum community began to distinguish between L2-solutions fully protected by the main Ethereum network and other scaling options with its consensus mechanisms-sides.
According to him, many sidespecks use the consensus mechanism that limits the number of subjects that have the opportunity to verify data. For example, in the case of Delegated-Proof-Of-Stake, only 21 validator usually operates, their number is small and the systems based on Proof-OF-Abority.
“In Polygon Pos Chain, everyone can join the network and begin to validate its condition. This is important, since any participant has the opportunity to become a validator and independently check the correctness of transaction processing, ”Jakub explained. – This model allows anyone to participate in ensuring the security of the network with any number of Matic tokens ".
As mentioned earlier, validation is carried out by a certain part of the manufacturers of the BOR network blocks. The latter periodically "shuffle" the validators Heimdall. Selected network participants validate blocks only certain block sets (span). After that, a new selection process starts. This is a specific feature of Polygon.
“This does not happen to the detriment of the speed of transactions, since all validators do not need to constantly check the blocks,” the founder of the Finematics project emphasized.
What bridges lead to Polygon?
Heimdall validators make possible decentralized cross-transfer cross-transfer between Ethereum and Polygon. There are two types of bridges for this – Plasma and POS.
Initially, the project used only the Plasma bridge, which is characterized by a high level of security. Its main drawback is the seven -day period of the withdrawal of assets that many users might seem too long.
Then the developers presented a POS-bridge designed to solve the problem of long-term conclusions of funds. This tool is much faster, but less safe – it implies users’ trust in validators.
There are also bridges from third -party projects. For example, Zapper Bridge, working only in the direction from Ethereum to Polygon. Connext XPollinate Service supports the translation of crypto acts between ecosystems of XDAI, Polygon, Fantom and Binance Smart Chain. Similar functionality is provided by the bridge from the income aggregator Evodefi.
When interacting with bridges, users send crypto assets to them and receive equivalent coins based on another network.
To date, many decentralized systems have been developed, http://coin-graph.site/?p=21 between which there are significant technical differences. Such bridges play an important role-they make the Defi segment more liquid, active and less fragmented.
conclusions
The Polygon team actively develops advanced scaling solutions and invests multimillion -dollar products in Defi development. The result is – many well -known projects, including AAVE, Curve and Sushiswap, integrated with the new ecosystem. This allowed them to become more liquid and strengthen the market position.
Many new applications have been created that rely on cheap and quick transactions using Matic. The price of the latter due to high demand and the network effect over the year increased by more than 5000%.
Polygon allows the industry participants who do not have large means to experiment, shifting funds between different platforms like the details of the Lego designer. Fast and extremely cheap transactions open to users rather complex investment strategies using platforms like StakeDao, where various protocols are involved.
The team has a difficult task-one of the first to implement ZK-Rollups, Optimistic Rollups and other advanced developments. If successful, the project will become a central element of the EVM-compatible L2 solutions and justifies itself as a “scaling aggregator”. This should be facilitated by the advantage of the pioneer and the obvious directions of the development of the Defi segment towards interactiveness, minimize transaction costs and the fastest transactions.
On the other hand, competitors are not asleep – significant capital enters viable alternatives like Binance Smart Chain and Solana Gagarin News . These ecosystems also have impressive TVL indicators – $ 8.57 billion and $ 1.1 billion, respectively (as of 25.07.2021).
Who will win in this arms race will tell time. In any case, competition will not damage the further development of the industry.
Subscribe to FORKLOG news in Telegram: Forklog Feed – the whole news feed, FORKLOG – the most important news, infographics and opinions.



















